Understanding the Vulnerability of the Elderly Population
With advancing age comes a series of physiological changes that can increase the risk of accidents and injuries in the elderly. This population is more prone to falls, injuries, and accidents due to a range of factors, including decreased muscle strength, impaired vision and balance, and chronic conditions like osteoporosis and arthritis. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reports that one in four older adults falls each year, leading to serious injuries like hip fractures and head traumas.
Common Health Conditions in the Elderly
Chronic diseases such as heart disease, cancer, diabetes, stroke, and Alzheimer’s disease are more common in older adults, according to the National Institute on Aging. These conditions can limit mobility and cognitive function, thereby increasing the risk of accidents and injuries.
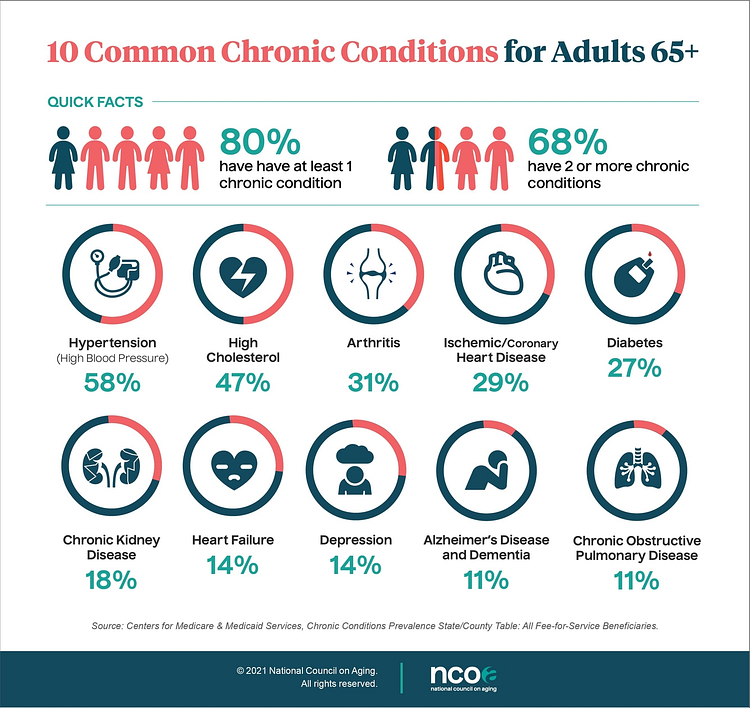
To mitigate these risks, it’s crucial to understand these vulnerabilities and take preventive measures. In the next section, we will explore practical strategies for preventing common accidents and injuries in the elderly population.
Recognizing Common Types of Accidents and Injuries
Being aware of the most frequent types of accidents and injuries can empower us to take precautions. Recognizing these common circumstances can also help us respond more effectively when incidents occur.
Falls and Fractures
According to the CDC, falls are the leading cause of both fatal and nonfatal injuries in older adults. Common fractures from falls include hip, wrist, and spine fractures.

Burns and Scalds
These injuries often occur in the kitchen or workplace. The American Burn Association provides resources on prevention and treatment.
Choking and Suffocation
Choking is a leading cause of injury and death among children, especially those aged 3 or younger. The American Red Cross offers courses on how to prevent and respond to choking incidents.
Motor Vehicle Accidents
The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration reports that in 2019, over 36,000 people died in motor vehicle crashes.

Strategies for Fall Prevention
Falls are a significant health risk for the elderly, leading to injuries and decreased quality of life. However, they can be prevented with effective strategies.
Regular Physical Activity
Engaging in regular physical activity is essential for improving strength and balance. Activities such as Tai Chi, Yoga, and resistance training can enhance muscle strength and flexibility, reducing the risk of falls.

Home Safety Measures
Ensuring home safety can prevent tripping and slipping incidents. Remove clutter, secure loose rugs, improve lighting, and install handrails where necessary. Fall-proofing your home is a crucial step in accident prevention.

Vision Checks and Proper Footwear
Regular vision checks can detect vision problems early, reducing the risk of falls caused by poor sight. Similarly, wearing appropriate, non-slip footwear can significantly decrease the chances of slipping.

Ensuring Safe Cooking and Heating Practices
As we age, our physical and cognitive abilities may undergo changes, making us more susceptible to accidents and injuries. One common area where this risk is amplified is in the kitchen and during heating practices. Statistics reveal that cooking fires are the leading cause of home fires and injuries, hence the importance of safe cooking cannot be overstated.

Fire Safety Tips for the Elderly
As our loved ones age, it is crucial to educate them on fire safety measures. These include never leaving the kitchen unattended while cooking, keeping flammable items away from the stove or heater, and ensuring all appliances are switched off after use. The U.S. Fire Administration provides comprehensive fire safety tips specifically for the elderly.
Smoke Alarms and Fire Extinguishers: Lifesavers in Your Home
Smoke alarms and fire extinguishers play a vital role in preventing fires and minimizing damage. Smoke alarms provide early warning signs, while fire extinguishers can help suppress small fires before they spread. Regular checks and maintenance of these devices are essential for their effective functioning. The American Red Cross provides valuable information on these lifesaving tools.

Preventing Choking and Suffocation
As our loved ones age, their risk for accidents and injuries increase. One area that requires substantial attention is preventing choking and suffocation, particularly related to safe eating practices, proper use of medical devices, and regular check-ups for respiratory conditions.
Safe eating practices for the elderly
For the elderly, a simple meal can lead to a choking incident. Hence, it is crucial to ensure safe eating practices. The National Institute on Aging recommends small, chewed bites, avoiding dry foods, and always eating in an upright position.
Proper use of medical devices like CPAP machines
Medical devices such as CPAP machines for sleep apnea can present suffocation risks if not used correctly. Regular maintenance and proper handling, as advised by the FDA, can mitigate these risks.

Importance of regular check-ups for respiratory conditions
Regular check-ups are vital in managing respiratory conditions and preventing complications. The American Lung Association emphasizes the need for routine visits to monitor lung health and adjust treatment plans as necessary.
Road Safety for the Elderly: A Critical Component of Accident Prevention
Senior citizens face unique challenges when it comes to road safety. Regular eye and ear checks are crucial to maintaining safe driving habits. The American Academy of Ophthalmology emphasizes that age-related vision changes can significantly impact driving abilities. Similarly, hearing loss, prevalent in 25% of seniors over 65 according to NIDCD, can hinder awareness of crucial auditory signals on the road. Regular screenings help identify and manage these changes, contributing to safer driving.
Understanding Limitations and the Right Time to Stop Driving
Self-awareness is another critical aspect of road safety. Seniors must acknowledge when driving becomes risky due to health issues, slower reflexes, or cognitive decline. The National Institute on Aging provides resources to help seniors understand when it may be time to stop driving.
Embracing Alternatives: Public Transport and Ride-Sharing Services
When driving is no longer safe, seniors can turn to public transport or ride-sharing services, like Uber or Lyft. These options maintain their independence and mobility without compromising safety.

Role of Caregivers in Accident Prevention
As primary support for seniors, caregivers play an instrumental role in accident prevention. They initiate and enforce safety protocols, ensuring a secure environment. From installing non-slip mats in restrooms to arranging furniture for unobstructed movement, caregivers significantly reduce accident risks. CDC’s guidelines on preventing falls offer useful insights.
Underscoring Regular Health Checks
Regular health checks for the elderly are not just important, they’re vital. These routine assessments help detect potential health issues early, reducing the risk of falls and injuries. Caregivers can manage these health checks, ensuring seniors are in optimal health. The National Institute on Aging provides valuable resources on this topic.

Providing Emotional and Psychological Support
Fear of accidents can induce stress and anxiety in seniors, increasing the risk of falls. By offering emotional and psychological support, caregivers can alleviate these fears, encouraging a more confident and self-assured demeanor. American Psychological Association’s guidelines on elderly mental health are a valuable resource.

Conclusion: Building a Safer Environment for the Elderly
In the endeavor to prevent common accidents and injuries in the elderly population, we’ve unraveled several key strategies. Ranging from home modifications, such as eliminating tripping hazards and installing handrails, to promoting regular physical activity to enhance balance and strength.
But more than individual efforts, there is a pressing need for a collective societal responsibility. We need to advocate for safer public spaces and influence policy to prioritize elder safety. The onus is on us to ensure that our elders can navigate their environment without fear of injury.
Lastly, the importance of continuous research and innovation in elder care cannot be overstated. With the aid of technology and innovative solutions, we can provide better care and safety for our aging population.
By fostering a comprehensive understanding of these strategies and advocating for societal changes, we can build a safer and more inclusive environment for the elderly.